
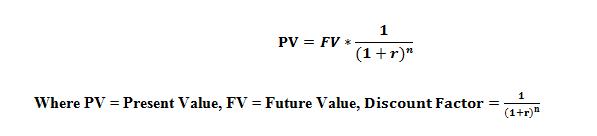
Spread – The difference between two interest rates.Inverse correlation is sometimes known as a negative correlation, which describes the same type of relationship between variables. Positive correlation describes the relationship between two variables which change together, while an inverse correlation describes the relationship between two variables which change in opposing directions. Correlation – Variables are correlated if the change in one is followed by a change in the other.Mortgage rates are determined by the lender and can be either fixed, staying the same for the term of the mortgage, or variable, fluctuating with a benchmark interest rate. Mortgage Rate – The rate of interest charged on a mortgage.government pays to borrow money for different lengths of time. Looked at another way, the Treasury yield is the effective interest rate that the U.S. Treasury Yield – The return on investment, expressed as a percentage, on the U.S.The risk-free rate represents the interest an investor would expect from an absolutely risk-free investment over a specified period of time. Risk-Free Rate of Return – The theoretical rate of return of an investment with zero risk.
Discount rate it free#
As noted, the highlighted input below refers to the risk free rate and the starting point of our build-up approach.īefore we dig in to comparisons let us define some common terms that we will use in our discussion A highlight of how we build up both the cost of equity and the weighted cost of capital is pictured below. debt), the difference in risk between large and small public companies, and the risk of the specific investment (subject company) vs. Risk premiums cover the incremental risk of equity investments in large-company stocks (vs. In determining the cost of equity, we use the build-up method which starts with a risk-free rate and adds risk components appropriate to the Company to arrive at a total discount rate. The appropriate discount rate should be the expected rate of return available on alternative investment opportunities with comparable risk. The determination of this rate puts the appraiser in the role of surrogate analyst for a hypothetical, informed, typically motivated, arms-length financial buyer. The rate of return used to discount projected future income to present value must be a reasonable estimate of the return needed to attract the capital of a willing buyer in the marketplace given the level of risk inherent Company. Over the next few weeks, I will dig into the five key inputs that go into a discount rate. Most often in our practice, this equity is attached to a private business that is owner operated. This discount rate is the expected rate of return on the subject interest which in most cases is the equity in the value of an operating business. One of the most important inputs surrounding the valuation of the business is the discount rate that is used in the analysis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
